The area of Iran is 1,648,195 Km2 which makes it the 17th largest country in the world. Iran is divided into 30 provinces and 336 districts. Tehran, the capital of Iran, is one of the most populous cities in the world, holding a population of 9 million. Iran is bordered on the East by Pakistan and Afghanistan, on the North by Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan, and Armenia as well as the Caspian Sea, on the west by Turkey and Iraq, and on the south by the Persian Gulf and the sea of Oman. Iran with a population of almost 70 million, of which more than 65% are urban dwellers, stands as the 17th populous country in the world.1 Iran’s population is young; almost one third of the population is less than 15 years old and only almost 5% is over 60 years. The population annual growth rate in 2006 was 1.2%. More than 95% of Iranians are Muslim. Iran has an important position in international energy production and reserves of oil and natural gas. Iran is the fourth producer and the fifth exporter of oil and has the third main proved reserves of oil in the world. It is also the fifth producer and has the second proved reserves of gas in the world. Industry and agriculture are other important contributors to Iran’s economy. Iran’s gross domestic product (GDP) at purchasing power parity (PPP) per capita was 9,200, 9,800, and 11,700 US $ in 2005, 2006, and 2007 respectively. As an important point, Article 29 of the Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran emphasizes that every Iranian has the right to enjoy the highest attainable level of health. The Ministry of Health and Medical Education is mandated to fulfill this goal through designing and implementing a national-level health policy. Yet, the Ministry of Health and Medical Education delegates its implementation to medical universities across the country. There is at least one medical university in every province. The president of a medical university is the highest health authority in the province who reports to the Minister of Health and Medical Education. The president of the medical university is in charge of public health, health care provision in public facilities, and medical education. Health care and public health services are provided through a nation-wide network. This network consists of a referral system, starting at primary care centers in the periphery going through secondary-level hospitals in the provincial capital and tertiary hospitals in major cities. The public sector provides primary, secondary, and tertiary health services. The emphasis of the government on primary health care over the last two decades has made the public sector the main provider of primary health care services across the country. Some primary health care services such as prenatal care and vaccination are provided free of charge in public facilities. The public sector also provides a considerable part of secondary and tertiary health services in the province. The private sector plays a significant role in health care provision in Iran. The private sector mainly focuses on secondary and tertiary health care in urban areas. There are many nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) active in health issues in Iran. NGOs are mainly active in special fields like children with cancer, breast cancer, diabetes, thalassemia, and so on.
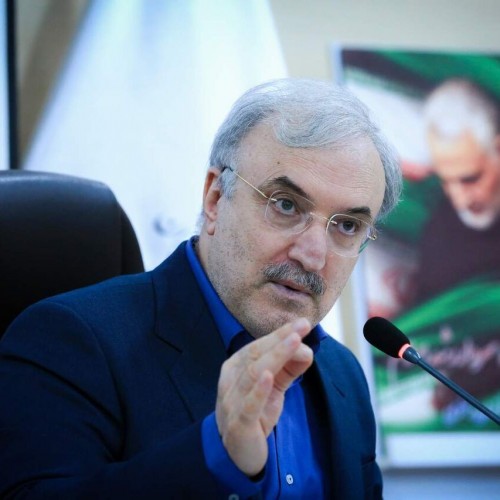
 Iranian Health Minister Shares Glad Tidings of Corona Vaccine: Native Vaccine Ready in Spring
Iranian Health Minister Shares Glad Tidings of Corona Vaccine: Native Vaccine Ready in Spring